data replication
What is data replication?
Data replication is the process of copying data from one location to another. The technology helps an organization maintain up-to-date copies of its data in the event of a disaster.
Replication can take place over a storage area network, local area network or local wide area network as well as to the cloud. For disaster recovery (DR) purposes, replication typically occurs between a primary storage location and a secondary offsite location.
Approaches to data replication
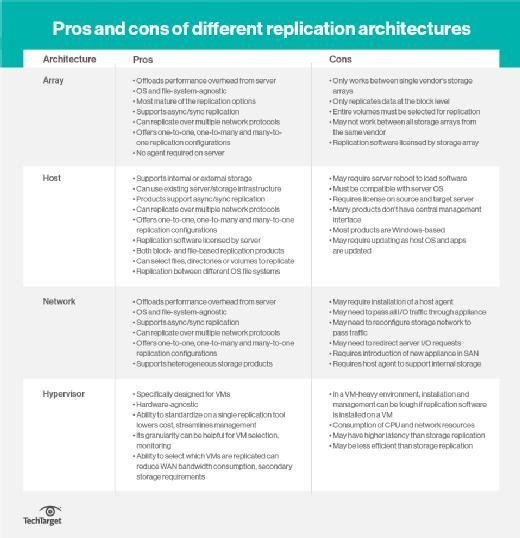
There are four places where replication can happen: in the host, in the hypervisor, in the storage array or in the network. Array-based replication once was the dominant method, but the others have gained in popularity.
Host-based replication uses servers to copy data from one site to another, using software on application servers. It is usually file-based and asynchronous. Host-based replication software includes capacities such as deduplication, compression, encryption and throttling.
Hypervisor-based replication is a type of host-based replication that replicates entire virtual machines from one host server or host cluster to another. Because it is specifically designed for VMs, hypervisor replication makes it easy to fail over to the replicate if the primary copy of the VM is lost. It can also run on servers that do not natively support replication. All host-based replication uses CPU resources, which might affect server performance.
Array-based replication lets compatible storage arrays use built-in software to automatically copy data between arrays. Array-based replication is more resilient and requires little cross-departmental coordination when deployed. But it is limited to homogeneous storage environments, as it requires similar source and target arrays.
Network-based replication requires an extra switch or appliance between storage arrays and servers. Network-based replication typically takes place in heterogeneous storage environments -- it works with any array and supports any host platform. There are fewer network-based replication products on the market compared to array- and host-based offerings.
Synchronous vs. asynchronous data replication
Data replication can be synchronous or asynchronous depending on when it takes place.
Synchronous replication takes place in real time, and is preferred for applications with low recovery time objectives that can't lose data. It's primarily used with high-end transactional applications that require instantaneous failover in the event of a failure. This replication approach is more expensive and creates latency that slows the primary application.
Synchronous replication is supported by array-based and most network-based replication products, but rarely in host-based ones.
Asynchronous replication is time-delayed. It is designed to work over distances and requires less bandwidth.
This replication is intended for businesses that can withstand lengthier recovery point objectives. Because there is a delay in the copy time, the two data copies might not always be identical. Asynchronous replication is supported by array-, network- and host-based replication products.
Data replication with other technologies
Data replication is a key technology for disaster recovery. It is often combined with snapshot technology, which lets users replicate data periodically while still being able to roll back to a specific point in time for recovery. Deduplication -- which eliminates redundant data -- is also frequently combined with replication for DR and backup. Dedupe helps replication by requiring less data to move across the network.
An organization should test its replication to ensure there is enough bandwidth and that the appropriate data is copied. Administrators must also make sure that the available infrastructure can replicate data quickly enough to keep up with data growth and the data change rate.
A backup administrator must consider the volume of the data being replicated, especially if the organization performs replication to a remote data center. Synchronizing large amounts of data across a low-speed connection might not be practical. Seeding -- copying data to removable media and then to the target device -- might be the better option.








