disaster recovery (DR) site
What is a disaster recovery (DR) site?
A disaster recovery (DR) site is a facility an organization can use to recover and restore its technology infrastructure and operations when its primary data center becomes unavailable.
The decision about what kind of DR site an organization needs and its location requires careful planning and a balance of costs against any risks. Disaster recovery sites should be a part of a business continuity plan.
Hot, warm and cold disaster recovery sites
How long it would take a disaster recovery site to replace the service in the event of a failure is usually expressed by how hot or cold it is.
- At a hot site, an organization has access to a fully functional data center with hardware and software, personnel and data. It is typically kept ready around the clock and can immediately respond in the event of a disaster. Hot sites can respond to failures and replace a primary site in milliseconds to hours.
- A warm site is an equipped data center but does not have live data. It contains some or all the equipment found in a working data center, such as hardware, software, network services, and personnel. An organization can install additional equipment and introduce customer data when a disaster occurs to make up for any shortfall. Warm sites can respond to outages in hours to days.
- A cold site has infrastructure to support IT systems and data, but no technology until an organization activates DR plans and installs equipment. A cold site is only an option for business systems that can be down for an extended period or to build out capacity when other DR sites are in operation. An organization can use a cold site to supplement hot and warm sites in the event of a disaster that lasts a long time. Cold sites might take weeks to months to come fully online.
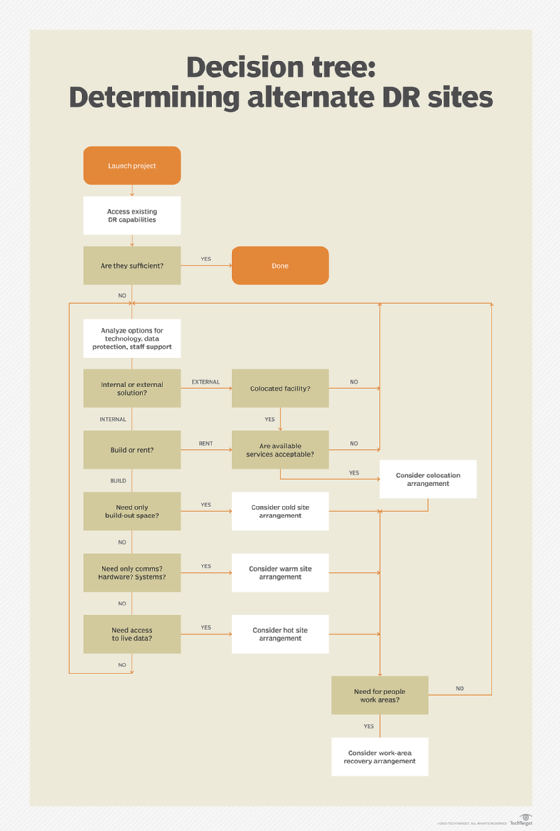
Internal vs. external disaster recovery sites
Disaster recovery sites are classified as either internal or external. Internal sites are owned and maintained by the organization. External sites are owned and operated by an outside provider.
Internal DR sites are a good fit for companies with large information requirements and aggressive recovery time objectives. The additional data centers are used to maintain high availability of the data and resources. The internal site is typically a second data center and allows a company to recover and resume operations following a disaster at the primary center. Maintaining a second data center can be quite costly, but it might be worth it if the loss of service would result in massive financial loss.
Most internal DR sites are hot sites. They might also be used to load balance or provide better service to a geographic region during normal operation but are sized appropriately to handle the full load should one site become unavailable.
External DR sites are cheaper to operate but might take longer to respond to an outage. These can range in service from full management with DR as a service (DRaaS) to simple rentable empty data centers (cold sites).
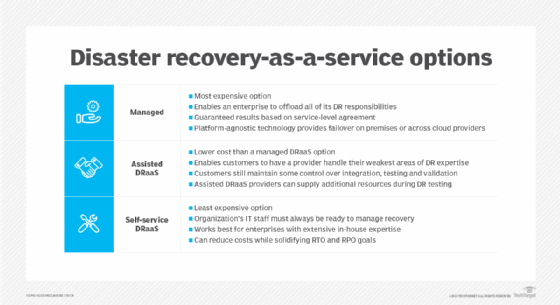
A company can also use a cloud-based recovery site. Having DR sites in the cloud reduces the need for data center space, infrastructure and resources. Cloud DR sites can be cheaper and more viable for smaller companies, but security and bandwidth are concerns.
Other types of DR sites include mobile recovery services and colocation data centers. Mobile recovery services -- for companies that want to remain in the area of the disaster -- typically involve specially outfitted trailers that are positioned at pre-arranged locations. At colocation data centers, or carrier hotels, multiple customers install network, server and data storage devices, and connect to a variety of telecommunications and network service providers.
Selecting a disaster recovery site
Many factors must be considered when considering where to locate a DR site. These factors can also be used to evaluate the suitability of external or could DR sites. These factors will often involve tradeoffs, so considering the recovery objectives and business continuity is essential.
Businesses often prepare for minor disruptions, but it's easy to overlook larger and more intricate disasters. Examine the top scenarios for IT disasters that disaster recovery teams should test vigorously.






